
As the technology for new energy electric vehicles (EVs) advances rapidly, DC-DC converters have become increasingly critical components in these vehicles. Modern electric vehicles rely on DC-DC converters to bridge voltage gaps between 400-800V traction batteries and 12/48V auxiliary systems. These components achieve 96-98% conversion efficiency (Texas Instruments 2023 report), manage the main power battery, enhance overall energy efficiency, and ensure seamless power delivery from propulsion to infotainment subsystems.
DC-DC converters (or DC-DC power supplies) convert one DC voltage level to another. They use electronic switching elements like transistors and energy storage components such as inductors and capacitors to achieve high efficiency and stable voltage output.
These converters precisely regulate output voltage by adjusting the duty cycle of electronic switches, ensuring compatibility with varying load demands. Engineers consider conversion efficiency—the ratio of input power to output power—a key performance metric because it directly impacts energy utilization and system heat dissipation.
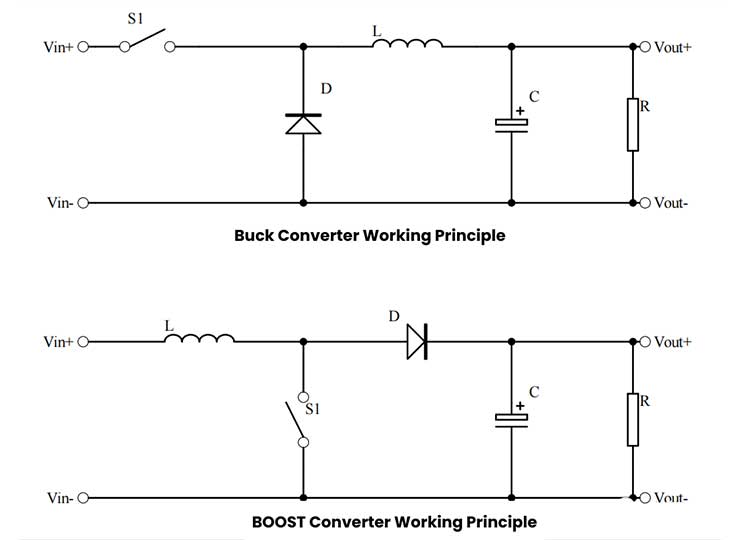
DC-DC converters are categorized into two main types:
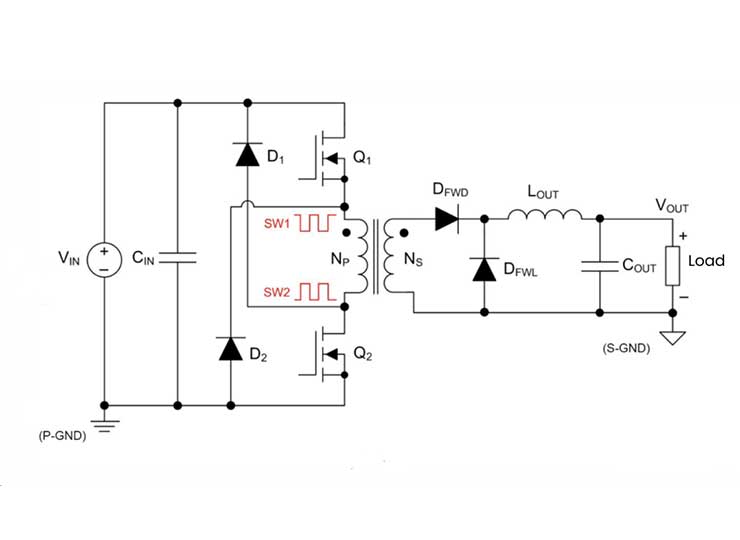
In new energy electric vehicles, DC-DC converters perform critical functions in battery management systems. These converters actively manage and distribute electrical energy between the battery and the vehicle's electronic systems while maintaining proper voltage matching during charging.
For example, DC-DC converters step down high voltage from power batteries (such as lithium-ion batteries) to charge lead-acid batteries at their required voltage levels. In drive systems, they deliver stable, efficient power from the high-voltage main battery to the electric motor. For auxiliary systems like air conditioning and lighting, the converters regulate and distribute power as needed.
Solutions to these challenges include optimizing heat sink designs, employing high-efficiency switching components, utilizing high-frequency switching techniques, and integrating high-voltage components with advanced isolation technologies.
Advancements in materials and technologies, such as gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors, are significantly improving the energy conversion efficiency and compactness of DC-DC converters. These innovations are vital for the continued development of the electric vehicle industry.
Ongoing innovation and technological advancements will drive the future of DC-DC power supplies in electric vehicles. These converters boost energy efficiency while strengthening vehicle performance and reliability. Engineers must thoroughly understand DC-DC power supplies to optimize and design cutting-edge electric vehicles.