
Understanding the intricate workings of EV charging system is crucial for maximizing vehicle performance and reliability. Central to this discussion are the various components that make up the charging infrastructure of pure electric vehicles.
The charging system of pure electric vehicles comprises several critical components, including an On-Board Charger (OBC), charging interfaces, a DC/DC converter, and associated wiring. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring efficient and safe charging.
The primary function of the OBC is to convert AC power from the grid (typically 240V, varying by region) into high-voltage DC power for charging the traction battery. What's more, the OBC also provides essential protective measures such as overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, and undercurrent protections. For example, In case of any anomalies, the system promptly cuts off power supply to prevent damage. Both the DC charger and OBC can initiate an emergency shutdown during charging if necessary.
The DC/DC converter transforms the high voltage from the traction battery into 12V low voltage electricity to power the vehicle's auxiliary systems. This conversion is crucial for maintaining the functionality of various electronic components within the vehicle.
Electric vehicle charging systems are categorized into two types: AC Charging (Slow Charging) and DC Charging (Fast Charging).
Slow charging utilizes single-phase AC household electricity, which is rectified and converted into high-voltage DC power to charge the traction battery. Key components include:
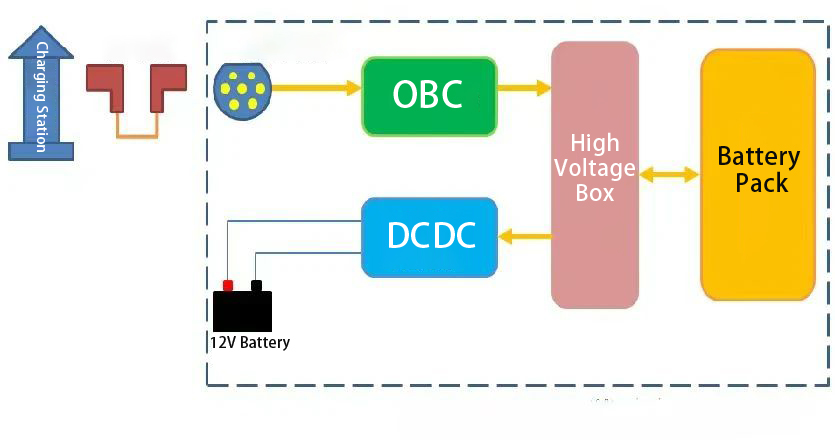
Now let's move on to DC charging systems, also known as fast or emergency charging, charge electric vehicles using high currents (150-400A). This enables rapid recharging within a short period, crucial for time-sensitive operational vehicles. These systems typically use industrial three-phase 400V electricity (varying by region), which is converted to high voltage and current to directly charge the vehicle's traction battery.
Key components include:
Upon connecting the charger to the vehicle, the Battery Management System (BMS) receives a wake-up signal and sends the appropriate charging current instructions. The BMS then engages the high-voltage relays, initiating battery charging. One hour of DC charging can achieve up to 80% battery capacity.
Some Level 3 charging stations in Europe and America offer up to 400kW, providing an additional range of 300 kilometers in just 15 minutes.
By leveraging advanced fast charging technologies, electric vehicle operators can enhance their fleet efficiency and reduce operational disruptions, contributing to a more sustainable and reliable transportation ecosystem.
Enhancing the charging experience is pivotal for accelerating EV adoption. Key factors include the ease of finding charging stations and charging speed. Currently, it takes 1.5 to 2 hours to recharge an EV from 10% to 100%, indicating significant room for improvement towards achieving refueling times comparable to gasoline vehicles (around 15 minutes).
High-voltage platforms are becoming standard among OEMs, enabling higher charging powers and shorter durations under similar currents. In China, many vehicles now support 800V platforms, with some companies developing 600kW charging systems capable of 1000V and 600A.
The 800V platform is rapidly advancing, with potential future developments targeting even higher voltages like 1200V. Post-2024, high-power charging stations will play a critical role in meeting the fast-charging demands of EVs, driving further industry growth.
For the latest news please view Brogen’s Linkedin. For more videos please click Brogen’s Youtube.