
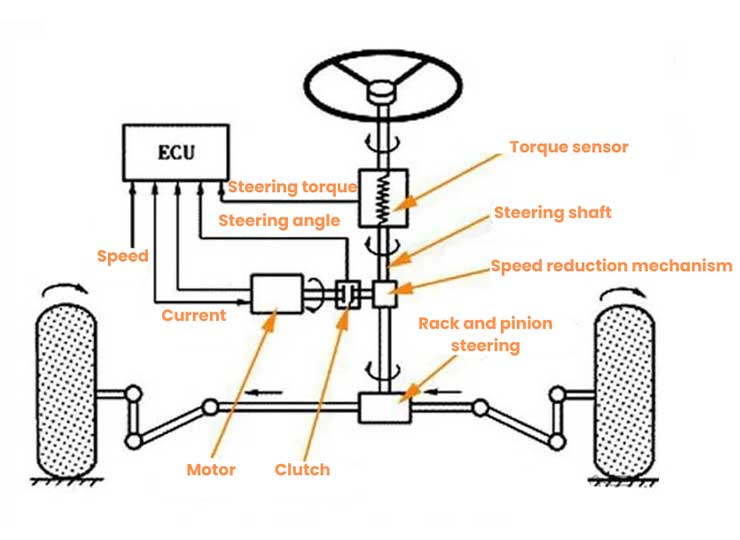
The EPS (Electric Power Steering) system is an advanced steering system that integrates mechanical steering, electronic sensing, control, and drive technologies. It primarily consists of the following components: the mechanical steering system, steering torque sensor, vehicle speed sensor, electronic control unit (ECU), motor, and reduction gear mechanism.
The working principle of EPS is relatively complex but highly efficient. When the driver turns the steering wheel, the torque sensor detects this action and converts the resulting angular displacement into an electrical signal, which is then sent to the ECU. Simultaneously, the vehicle speed sensor transmits the vehicle speed information to the ECU. Upon receiving this information, the ECU processes it through a series of precise control algorithms to determine the motor's rotation direction and the optimal assist torque. The ECU then sends a control signal to the motor, which is driven by the power drive circuit. The motor's output, after torque enhancement through the reduction gear mechanism, drives the gear rack mechanism, providing steering assistance to the driver.
The motor is a crucial power source within the EPS system and significantly impacts EPS performance. The system requires the motor to have high torque, minimal torque fluctuation, low rotational inertia, high power density, as well as high reliability and long lifespan. Currently, Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) and Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) are widely used in various EPS systems due to their unique advantages, such as simple structure, reliable operation, easy maintenance, high operational efficiency, no excitation losses, and excellent speed regulation.
The EPS system can adjust the assist level in real-time based on vehicle speed, ensuring that the car is easy to steer at low speeds while remaining stable and reliable at high speeds. This characteristic makes EPS systems a key development direction for modern automotive steering systems.
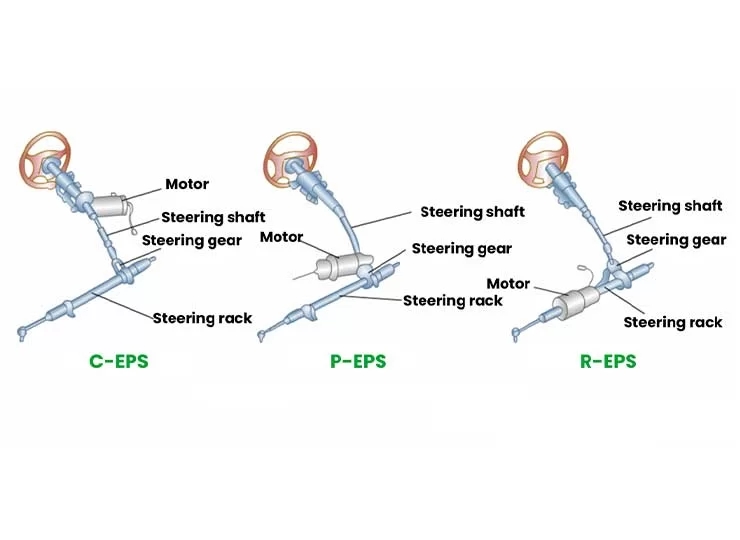
The Electric Power Steering (EPS) system can be categorized into three main types based on the motor's installation position and mechanical structure: Column Mounted, Pinion Mounted, and Rack Mounted.
In this EPS system, the assist motor is installed on the steering column and is connected to the steering shaft via a reduction gear mechanism, directly driving the steering shaft to achieve power-assisted steering. Due to its simple and compact structure, it is typically used in small and compact vehicles. However, since the assist motor is located inside the cabin, its size is relatively limited by space and noise constraints, and therefore, the output torque is also limited.
In this type of EPS, the assist motor and reduction gear mechanism are connected to the pinion, directly driving the gear to achieve power-assisted steering. Since the motor is not installed inside the passenger cabin, larger motors can be used to achieve higher assist torque without concerns about noise caused by motor inertia. This design allows Pinion Mounted EPS to provide stronger assist capabilities, making it suitable for a wide range of vehicles.
Rack Mounted EPS involves the assist motor and reduction gear mechanism directly driving the rack to provide power assistance. This design can offer greater assist torque, but the overall system structure is relatively complex and costly, making it suitable for high-end vehicles such as luxury cars and commercial vehicles.
In conclusion, different types of EPS systems each have their characteristics and applicable scenarios. The selection of an EPS system should be based on factors such as vehicle type, performance requirements, and cost considerations.
For the latest news please view Brogen’s Linkedin. For more videos please click Brogen’s Youtube.